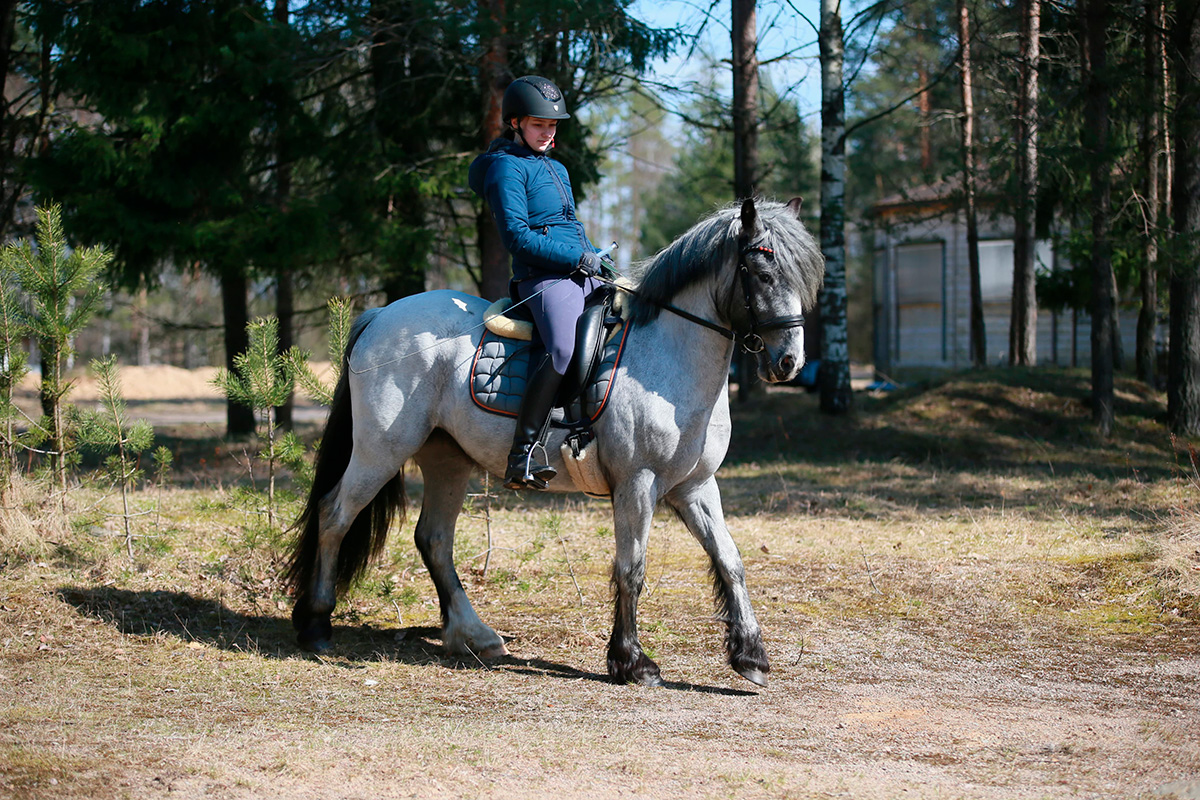
Any problems with a horse are caused by a human
Training will succeed only if there is mutual understanding between a human and a horse. Any problems in a horse’s behavior are related to human actions, and, for eliminating and preventing them, the person needs to pay attention to negative signals and look for their root cause.
These issues were covered by Katerina Berezina, a trainer for working with horses on the ground, a specialist in correcting the horse’s behavior, in her lecture «Six basic needs of a horse. How to prevent formation of abnormal behavior» to be delivered by the famous zoopsychologist as part of the business program of Day Two of the 25th International Equestrian Exhibition «Hipposphere».
People have only recently established that horses have feelings, emotions, empathy and consciousness. The first attempts to legally protect animals from cruel and inappropriate treatment were made only in the 19th century. Before that, people could do anything they liked with defenseless and unresponsive domestic horses. The first studies of horses’ needs were carried out even later: for example, it turned out that freedom of movement was vital for horses only at the end of the 20th century. At the same time, the document «5 freedoms», fundamental in the field of ethics of communication with animals, appeared. It establishes that horses should be freed from hunger, thirst, pain, discomfort, stress and have opportunities for natural behavior.
Following this document, scientists have deduced six basic needs of the horse. These are movement, access to food and water, social communication, rest in the herd, exploring the territory and the opportunity for escaping.
Katerina Berezina is sure that the abnormal behavior forms in the horse, if any of these needs is not met.
There are many elements of abnormal behavior, but each of them is a signal meaning that «not everything is okay», «I have something in pain», «I’m stressed», which the horse sends to its human owner.
The most common variants of abnormal behavior are eating disorders, aggressive behavior, as well as so-called stereotypical behavior, when actions performed by the horse are meaningless and unnatural for this species. For example, shaking its head, kicking walls or fences, slapping its lips, looping in a circle, biting and touching surfaces with its teeth are signs of stereotypical behavior, lists Katerina Berezina.
A horse, like a human, can suffer from depression. Its causes can be very different both in nature and in duration. Prolonged social isolation, chronic physical pain, boredom, learned helplessness, abuse, inconvenient neighbors or unsuccessful transportation may be causes of a horse’s depression, which forms the animal’s abnormal behavior.
If the owner has noticed negative signals and wants to help the horse, the best option is to step back, find the cause and eliminate it, and only then move on in the process of training and learning, advises Katerina Berezina. However, this can take quite a long time: sometimes it takes several months or even years for the horse and its human to cope with stress.

 Calendar
Calendar
 Online application
Online application
 Map
Map
 How to get
How to get



